Unlocking Agricultural Insights:
Utilizing Remote Sensing for Crop Type Classification
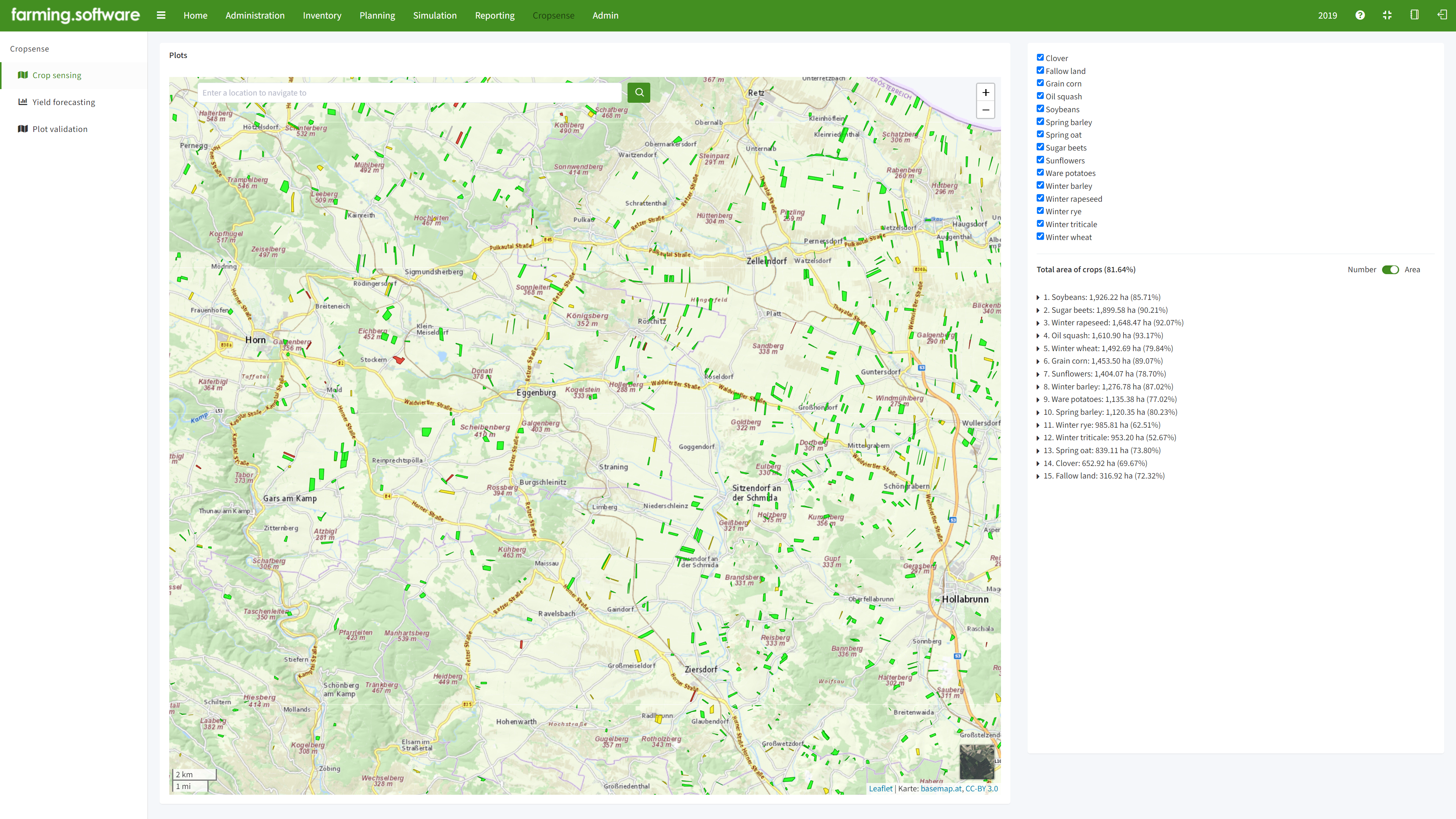
farming.software’s remote crop sensing module uses remote sensing, coupled with machine learning, to identify crops with high accuracy, providing valuable information for agricultural management and yield prediction.
Remote sensing has become a game-changer for precision agriculture, allowing farmers and researchers to identify crop types across vast areas. This information is crucial for improving crop yields, optimizing resource management, and monitoring crop health.
Satellites like Sentinel-2 and Landsat series capture multispectral images, revealing details beyond the visible spectrum. This allows scientists to analyze vegetation health through spectral indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index). We train advanced algorithms on massive datasets of remote sensing images combined with ground truth data (e.g., field observations). These algorithms can then identify crop types with high accuracy based on spectral characteristics, spatial patterns, and changes over time (temporal data).
Accordingly, our crop sensing models allow you to experiment with different management strategies virtually before implementing them in the field. By harnessing the power of our crop modelling software, you can:
- Knowing exactly what crops are growing where allows for targeted fertilizer and pesticide application, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Remote sensing enables large-scale monitoring of crop health, allowing early detection of stress or disease outbreaks.
- By analyzing historical data and current crop conditions, stakeholders can gain insights into potential crop yields, aiding in informed decisions.
Crop sensing is not only beneficial just for farmers. Remote sensing data on crop types can be a valuable tool for political decision makers in several ways:
- Food Security and Policy Planning: By identifying the location and extent of different crops, decision makers can gain insights into national food production capacity. This allows for informed policy decisions regarding food security, such as import/export quotas, strategic stockpiles, and agricultural subsidies.
- Disaster Management and Relief Efforts: To assess the extent of damage to agricultural land following natural disasters like floods, droughts, or extreme weather events. This information is crucial for directing emergency relief efforts and allocating resources efficiently to affected farmers.
- Monitoring Land Use and Sustainability: Tracking changes in crop types over time can reveal trends in land-use patterns. We are using this data , e.g., to identify areas of deforestation or unsustainable practices. This allows policymakers to develop regulations and incentives that promote sustainable agriculture.
- Trade Agreements and Market Analysis: Knowing the types and quantities of crops being grown in different regions can inform trade negotiations and agreements. Additionally, by analyzing historical data, decision makers can predict potential crop yields and market fluctuations, allowing for better trade strategies.
- Taxation and Agricultural Development: In some cases, crop type data can be used to improve the efficiency of agricultural tax collection and allocation of development funds. By identifying areas with specific crop types, decision makers can target support programs and subsidies to farmers who need them most.